CTF PRE
[dreamhack] level 1 아 문제 이름 뭘로하지 문제 풀이.. 본문

ida로 디컴파일 해보니 사용자에게 입력을 받고, s를 파라미터로 하는 함수인 sub_145A의 값이 참이면 correct 출력, 아니라면 wrong을 출력한다. 해당 문제는 어떤 값을 입력해야 correct가 나오는지 알아내야 하는 문제 같다.
sub_145A 함수 분석

만약 input 값의 길이가 39가 아니라면 0을 반환
v2~v7 : 순서대로 input + 8, 24, 32, 36, 38을 연산한 값을 저장
s1[0~3] : 순서대로 Input, v2, input + 16, v3를 저장
sub_1273 함수 호출
sub_139D 함수 호출
s1과 s2의 첫 0x27 바이트를 비교하여 결과가 0이라면 참(1)을 반환하고 아니라면 거짓(2)를 반환.
** main 함수에서 correct가 나오려면 memcmp 비교 결과가 0이어야 함. **
sub_1273 함수 분석

1바이트씩 해석함. 만약 i가 0x27보다 크거나 같으면 break
byte_2020[(unsigned __int8)(((-83 - (i & 7)) * ((i & 7) - 34)) ^ i)] + (*(_BYTE *)(s1 + i) ^ (unsigned __int8)(i + (-83 - (i & 7)) * ((i & 7) - 34))), (unsigned __int8)(i % 7) + 3 의 연산값을 인자로 하는 sub_123E 함수의 반환값을 v2에 저장
unsigned char ida_chars[] =
{
99, 124, 119, 123, 242, 107, 111, 197, 48, 1,
103, 43, 254, 215, 171, 118, 202, 130, 201, 125,
250, 89, 71, 240, 173, 212, 162, 175, 156, 164,
114, 192, 183, 253, 147, 38, 54, 63, 247, 204,
52, 165, 229, 241, 113, 216, 49, 21, 4, 199,
35, 195, 24, 150, 5, 154, 7, 18, 128, 226,
235, 39, 178, 117, 9, 131, 44, 26, 27, 110,
90, 160, 82, 59, 214, 179, 41, 227, 47, 132,
83, 209, 0, 237, 32, 252, 177, 91, 106, 203,
190, 57, 74, 76, 88, 207, 208, 239, 170, 251,
67, 77, 51, 133, 69, 249, 2, 127, 80, 60,
159, 168, 81, 163, 64, 143, 146, 157, 56, 245,
188, 182, 218, 33, 16, 255, 243, 210, 205, 12,
19, 236, 95, 151, 68, 23, 196, 167, 126, 61,
100, 93, 25, 115, 96, 129, 79, 220, 34, 42,
144, 136, 70, 238, 184, 20, 222, 94, 11, 219,
224, 50, 58, 10, 73, 6, 36, 92, 194, 211,
172, 98, 145, 149, 228, 121, 231, 200, 55, 109,
141, 213, 78, 169, 108, 86, 244, 234, 101, 122,
174, 8, 186, 120, 37, 46, 28, 166, 180, 198,
232, 221, 116, 31, 75, 189, 139, 138, 112, 62,
181, 102, 72, 3, 246, 14, 97, 53, 87, 185,
134, 193, 29, 158, 225, 248, 152, 17, 105, 217,
142, 148, 155, 30, 135, 233, 206, 85, 40, 223,
140, 161, 137, 13, 191, 230, 66, 104, 65, 153,
45, 15, 176, 84, 187, 22
};
sub_123E 함수 분석

해당 함수는 a1, a2에 대해. 비트 쉬프트 연산을 한다.
sub_139D 함수 분석
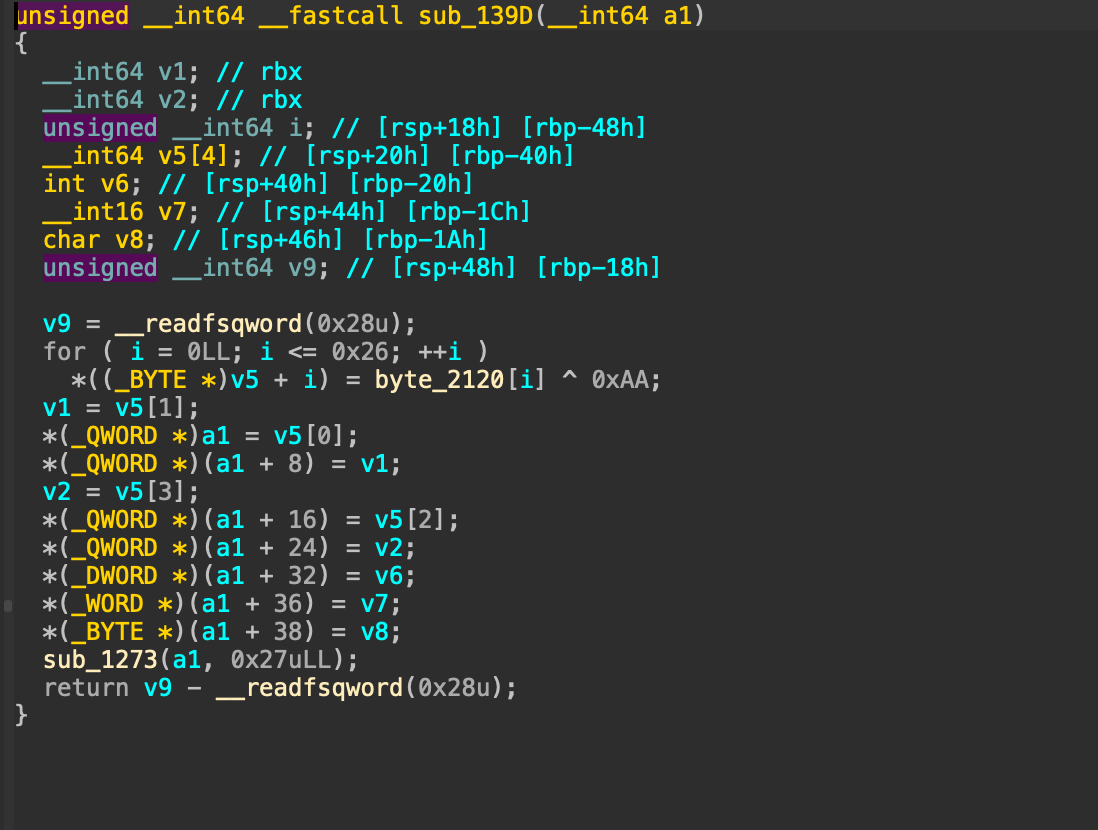
0x26만큼 반복하고 특정 연산을 한 뒤에 sub_1273 함수를 실행한다. 그리고 v9 - _readfsqword 연산을 수행한 값을 반환한다.
unsigned char ida_chars[] =
{
238, 226, 209, 250, 198, 207, 203, 217, 207, 245,
198, 197, 220, 207, 245, 222, 194, 207, 245, 237,
238, 245, 255, 232, 239, 248, 231, 239, 249, 226,
245, 203, 198, 200, 223, 199, 139, 139, 215
};
위의 함수들을 활용하여 모두 역연산하면 될 것 같다.
역연산 코드
def rotate_right(value, amount):
"""Rotate bits to the right (equivalent to sub_123E)
Handles negative shift counts by converting to positive"""
# Ensure amount is positive and within range
amount = amount % 8
return ((value >> amount) | (value << (8 - amount))) & 0xFF
def rotate_left(value, amount):
"""Rotate bits to the left (inverse of sub_123E)
Handles negative shift counts by converting to positive"""
# Ensure amount is positive and within range
amount = amount % 8
return ((value << amount) | (value >> (8 - amount))) & 0xFF
# S-box from the disassembly
byte_2020 = [
99, 124, 119, 123, 242, 107, 111, 197, 48, 1,
103, 43, 254, 215, 171, 118, 202, 130, 201, 125,
250, 89, 71, 240, 173, 212, 162, 175, 156, 164,
114, 192, 183, 253, 147, 38, 54, 63, 247, 204,
52, 165, 229, 241, 113, 216, 49, 21, 4, 199,
35, 195, 24, 150, 5, 154, 7, 18, 128, 226,
235, 39, 178, 117, 9, 131, 44, 26, 27, 110,
90, 160, 82, 59, 214, 179, 41, 227, 47, 132,
83, 209, 0, 237, 32, 252, 177, 91, 106, 203,
190, 57, 74, 76, 88, 207, 208, 239, 170, 251,
67, 77, 51, 133, 69, 249, 2, 127, 80, 60,
159, 168, 81, 163, 64, 143, 146, 157, 56, 245,
188, 182, 218, 33, 16, 255, 243, 210, 205, 12,
19, 236, 95, 151, 68, 23, 196, 167, 126, 61,
100, 93, 25, 115, 96, 129, 79, 220, 34, 42,
144, 136, 70, 238, 184, 20, 222, 94, 11, 219,
224, 50, 58, 10, 73, 6, 36, 92, 194, 211,
172, 98, 145, 149, 228, 121, 231, 200, 55, 109,
141, 213, 78, 169, 108, 86, 244, 234, 101, 122,
174, 8, 186, 120, 37, 46, 28, 166, 180, 198,
232, 221, 116, 31, 75, 189, 139, 138, 112, 62,
181, 102, 72, 3, 246, 14, 97, 53, 87, 185,
134, 193, 29, 158, 225, 248, 152, 17, 105, 217,
142, 148, 155, 30, 135, 233, 206, 85, 40, 223,
140, 161, 137, 13, 191, 230, 66, 104, 65, 153,
45, 15, 176, 84, 187, 22
]
# Target bytes from the disassembly
byte_2120 = [
238, 226, 209, 250, 198, 207, 203, 217, 207, 245,
198, 197, 220, 207, 245, 222, 194, 207, 245, 237,
238, 245, 255, 232, 239, 248, 231, 239, 249, 226,
245, 203, 198, 200, 223, 199, 139, 139, 215
]
def sub_123E(a1, a2):
"""Implementation of the sub_123E function according to the disassembly
Based on the assembly, this seems to be a right rotate:
return ((a1 >> a2) | (a1 << (8 - a2))) & 0xFF
But looking at the disassembly, it might actually be different.
Let's check the original code:
```
__int64 __fastcall sub_123E(unsigned __int8 a1, char a2)
{
return ((int)a1 >> a2) | (a1 << (8 - a2));
}
```
This seems to be a rotate right, but let's verify it's a right rotate.
"""
# Ensure a2 is a valid positive shift amount
a2 = a2 & 0x7 # Same as a2 % 8, but faster
return ((a1 >> a2) | (a1 << (8 - a2))) & 0xFF
def calculate_xor_value(i):
"""Calculate the XOR value used in sub_1273
This needs to match the assembly's computation exactly"""
# The assembly code: (-83 - (i & 7)) * ((i & 7) - 34)
# We need to make sure this matches the binary's computation
# Ensure we're doing the computation exactly as in the binary
term1 = (-83 - (i & 7)) & 0xFF # Keep in byte range
term2 = ((i & 7) - 34) & 0xFF # Keep in byte range
result = (term1 * term2) & 0xFF # Multiplication can overflow, so mask
return (result ^ i) & 0xFF
def sub_1273(s1, length):
"""Properly implemented sub_1273 function with correct byte range handling"""
v4 = 0
for i in range(length):
# Calculate the index into byte_2020
xor_value = calculate_xor_value(i)
index = xor_value & 0xFF
# Ensure index is in valid range
index = index % len(byte_2020)
# Get value from byte_2020 and calculate
sbox_value = byte_2020[index]
input_byte = s1[i]
i_plus_xor = (i + xor_value) & 0xFF
sum_value = (sbox_value + (input_byte ^ i_plus_xor)) & 0xFF
# Rotate the bits
rot_amount = (i % 7) + 3
v2 = sub_123E(sum_value, rot_amount)
# Update the current byte and v4
new_byte = ((i + v4) ^ ((3 * v2 + 7) & 0xFF)) & 0xFF
s1[i] = new_byte
v4 = new_byte
return length
def reverse_sub_1273(encrypted, length):
"""Reverse the transformations of sub_1273"""
original = bytearray(length)
v4 = 0
for i in range(length):
# Extract the current encrypted byte
encrypted_byte = encrypted[i]
# Recover what v2 would have been using the relationship:
# encrypted_byte = (i + v4) ^ (3 * v2 + 7)
v4_contribution = (i + v4) & 0xFF
target = (v4_contribution ^ encrypted_byte) & 0xFF
# Find v2 such that (3 * v2 + 7) & 0xFF == target
v2 = None
for test_v2 in range(256):
if ((3 * test_v2 + 7) & 0xFF) == target:
v2 = test_v2
break
if v2 is None:
raise ValueError(f"Could not find v2 for position {i}")
# Undo the rotation
rot_amount = (i % 7) + 3
# For rotate right with amount 'a', the inverse is rotate left with amount 'a'
unrotated = rotate_left(v2, rot_amount)
# Calculate the XOR value used in the original function
xor_value = calculate_xor_value(i)
# Find the sbox value
index = xor_value & 0xFF
index %= len(byte_2020)
sbox_value = byte_2020[index]
# Recover the original input byte
# We had: sum_value = (sbox_value + (input_byte ^ (i + xor_value))) & 0xFF
# And: unrotated = sum_value
# So: input_byte = (unrotated - sbox_value) ^ (i + xor_value)
i_plus_xor = (i + xor_value) & 0xFF
original_byte = ((unrotated - sbox_value) & 0xFF) ^ i_plus_xor
original[i] = original_byte
# Update v4 for the next iteration
v4 = encrypted_byte
return original
def main():
"""Main function to recover the flag"""
# First, XOR byte_2120 with 0xAA as done in sub_139D
expected = bytearray(39)
for i in range(39):
expected[i] = byte_2120[i] ^ 0xAA
# Create a copy for processing
processed = bytearray(expected)
# Apply sub_1273 to see what should match in the memcmp
sub_1273(processed, 0x27)
# Now reverse the process to get the original flag
flag_bytes = reverse_sub_1273(processed, 0x27)
# Convert to ASCII and print
flag = ''.join(chr(b) for b in flag_bytes)
print("Recovered flag:", flag)
# Verify our implementation is correct by applying sub_1273 to flag_bytes
verification = bytearray(flag_bytes)
sub_1273(verification, 0x27)
# This should match the processed buffer
if verification == processed:
print("Verification successful - our implementation is correct!")
else:
print("Verification failed - our implementation might be incorrect")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
flag : DH{Please_love_the_GD_UBERMESH_album!!}
